Edu Quality Assurance
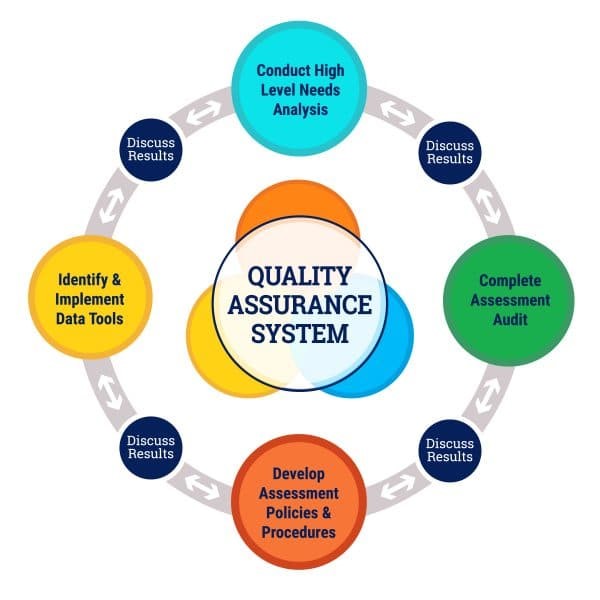
Quality assurance in Education and Quality Assurance System involves the systematic review of educational provision to maintain and improve its quality, equity and efficiency. It encompasses School/Academy/College/University self-evaluation, external evaluation (including inspection, quality audit, accreditation), assessment policies & procedures, data & tools, the evaluation of teachers & human resources, school/academy leaders, student assessments, analysis and assessment planning, programme evaluations etc.
Why Choose Online Education?
The overall objective of the quality assurance system in education is that the students should achieve the best possible learning outcomes and personal skills development in relevant educations and programmes that prepare them for working life and a society in change.
How can we improve the quality of education?
- Revise Educational Programs Based on Industry Changes.
- Retrain Faculty Staff.
- Take Advantage of Technology.
- Make Education More Collaborative.
- Focus on Student Retention.
- Encourage Student Empowerment.
- Engage with Parents or Guardians.
Ways to Improve Your University’s Quality of Education
- Hire a Qualified Lecturer.
- Measure the Student Outcomes and Improve.
- Provide Opportunities to Learn.
- Improve Teaching Methods.
- Introduce Innovative Infrastructure and Technology.
Education can be broken down into numerous areas of functionality:
- Curriculum and Content.
- Teaching and learning.
- Accreditation and assessment.
- Research and dissemination.
- Administration and leadership.
The Core Elements of Education Management may also review by the IEQAB Auditors:
1) Academic Quality and Morality/Integrity. 2) Teaching Staff Recruitment and Their Qualification scrutiny. 3) Delivery of Programs and review the program after degree/diploma attainment by the respective students/participants. 4) Offered Student Services and offered services evaluation. and 5) In case of Distance Learning Education/Online Education Provider, Website design and performance evaluation.
The 7 Teaching Principles:
The IEQAB also conforms about The 7 teaching principles, in 1987, Arthur W. Chickering and Zelda F. Gamson answered this question when they wrote “Seven Principles for Good Practice in Undergraduate Education.” They defined what good education means at the undergraduate level. The seven principles are based upon research on good teaching and learning in the college setting.
The 7 Teaching Principles: The first principle encourages contact between students and faculty. The second principle develops reciprocity and cooperation among students. The third principle promotes active learning techniques. The fourth principle requires the instructor to provide prompt feedback to students. The fifth principle emphasizes time on task. The sixth principle requires the instructor to communicate high expectations to students. The seventh and final principle requires the instructor to respect the diverse talents and ways of learning that the student body has to offer.
What is International Education? International education refers to a three (3) dynamic concept that involves a journey or movement of people, minds, or ideas across political and cultural frontiers.[1] It is facilitated by the globalization phenomenon, which increasingly erases the constraints of geography on economic, social and cultural arrangements.[2] The concept involves a broad range of learning, covering, for instance, formal education and informal learning (e.g. training, exchange programs, cross-cultural communication).[3] It could also involve a reorientation of academic outlook such as the pursuit of “worldmindedness” as a goal so that a school or its academic focus is considered international.
International education can be seen as developing ‘international-mindedness,’ or enhancing international attitude and awareness. From an ideological perspective, international education has a focus on moral development, by influencing the creation of “positive attitudes towards peace, international understanding and responsible world citizenship”.
Overall, international education can be viewed as the following:
- Promoting international understanding/international-mindedness and/or global awareness/understanding.
- Being active in global engagement/global or world citizenship.
- Increasing intercultural understanding and respect for difference.
- Encouraging tolerance and commitment to peace.
Educational Management? Educational management deals with organizing and coordinating people, material resources, and ideas in an educational establishment. These resources include teaching staff, non-teaching staff, students, parents, community members, and departmental officials. In addition to coordinating and organizing resources, educational management focuses on human resource management, which includes recruiting, hiring, and developing personnel for educational institutions. Educational management professionals use various organizational and managerial practices to achieve these goals.
Scope of Education management? The role of educational management is vital in determining the degree to which a particular educational program is achieving its goals, as well as in developing the people involved in the program. The scope of educational management covers all aspects of educational institutions, from organizing school facilities to maintaining records. Educational management also includes the coordination of activities for school-based health and physical education. In some cases, this role is divided into two sub-sectors: educational administration and human resource management.
The scope of educational management is as broad as the field itself. It encompasses all activities designed to achieve an educational goal, from the school level to the college or university level. The scope of educational management encompasses anything that is done to enhance the quality of education, including the supply of resources and the cultural and educational needs of a specific group. However, educational management’s scope is much broader than its definition’s boundaries.
For instance, educational
administration concerns itself with the development of human personality. As
such, it is particularly delicate in nature, requiring careful consideration of
the total life of a student. It means that educational administration requires
the participation of individuals from all aspects of life to be effective.
Despite the wide scope of educational administration, there are several key elements to this type of administration. To begin, it must identify the most important pieces of information and keep them in school district data systems. Then, it must analyze that information in order to generate a measurable statistic that represents the overall quality of an educational institution.
Eventually, educational management must address an educational institution’s financial and operational issues. Whether it is the budget, the teachers, the students, or the educational facilities, educational management deals with these issues and helps make decisions accordingly. It should also include the infrastructure and facilities of an educational institution, including office stationery, furniture, and a variety of other things. And while this field of study is broad, it is still in its infancy.
There are eight components of educational management, IEQAB strongly monitor and follow-up these areas of components during the IEQAB Accreditation tenure and IEQAB Unique process. The components are: (1) Educational Planning, (2) Educational Administration, (3) Educational Organisation, (4) Educational Direction, (5) Educational Co-ordination, (6) Educational Supervision, (7) Educational Controlling, and (8) Educational Evaluation.
